
Tables L1 and L2 in Appendix C show how to calculate the EML of individual lamps and larger spaces. During Performance Verification, EML is measured on the vertical plane at eye level of the occupant. The biological effects of light on humans can be measured in Equivalent Melanopic Lux (EML), a proposed alternate metric that is weighted to the ipRGCs instead of to the cones, which is the case with traditional lux. Through ipRGCs, lights of high frequency and intensity promote alertness, while the lack of this stimulus signals the body to reduce energy expenditure and prepare for rest. Table 2 shows the dependence of intensity (I) at a.

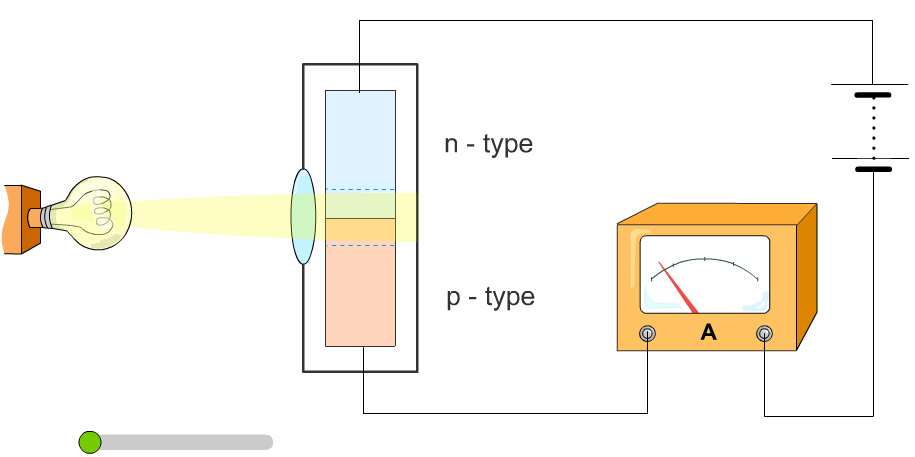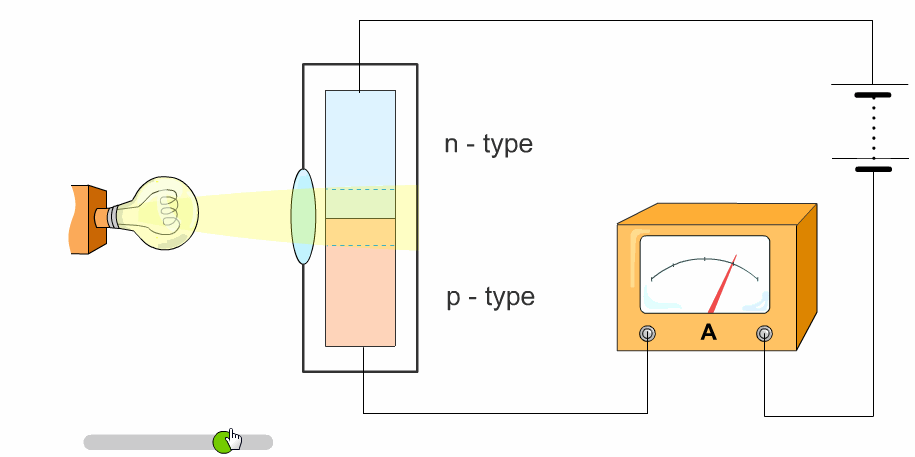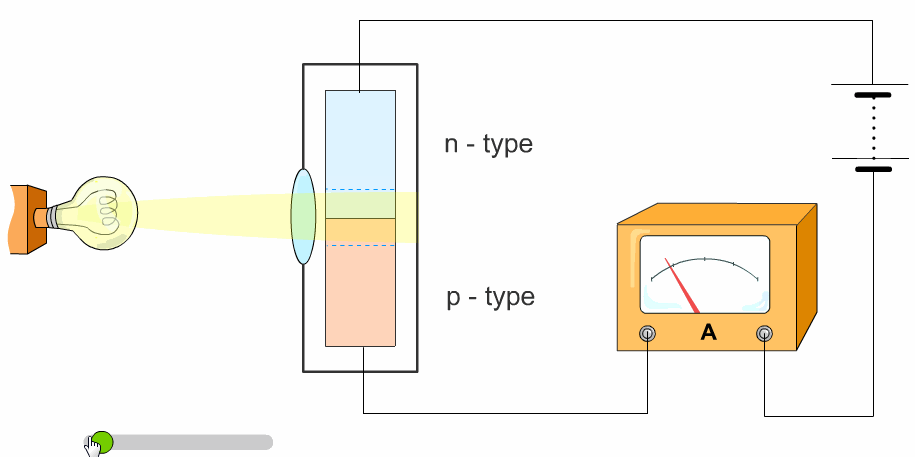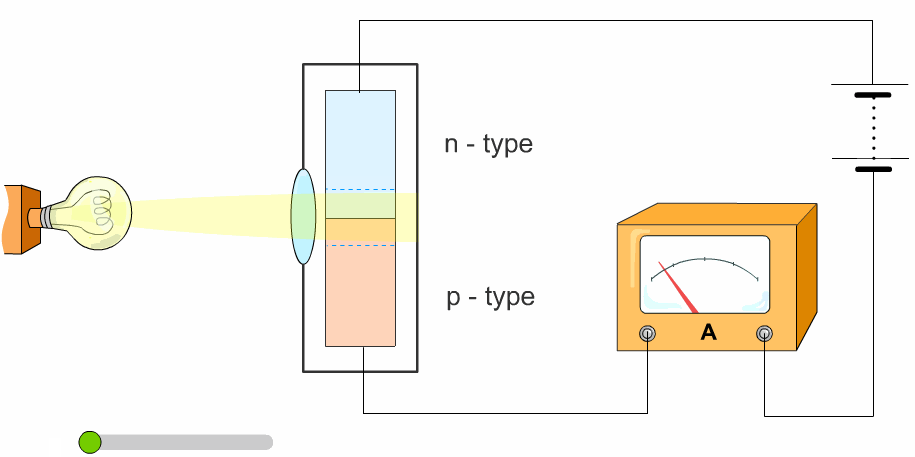
The light is brighter when it is higher in intensity. We think of relative intensity as a bright light. Light waves are less intense when spread out. Circadian rhythms are kept in sync by various cues, including light which the body responds to in a way facilitated by intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs): the eyes’ non-image- forming photoreceptors. The greater the intensity, the more energy is being transmitted. The intensity of the light decreases the further it travels from the lamp, but it also lights up a larger surface area. Obviously, a night light bulb will have a lower power rating than the light bulb used in a floor lamp. Light intensity is a measurement of the average power associated with waves, and is usually measured as the power per unit area. Light intensity is traditionally measured in lumens. In other words, a source of weak illuminance can generate the same amount of accumulated light as a powerful one if it’s given more time. But, if we run it for 10 seconds, we can still get that total light intensity is 1000mJ / cm². The greater the amplitude, the brighter the light. It runs with an illuminance of 1000 mW/cm ². Intensity Waves not only have length, but also have height, or amplitude. The type of measurement used depends heavily on the application. The green area in the table is our weak irradiator. There are many ways to measure intensity. In essence, it is how much light is being provided.
#Light intensity drivers
Light is one of the main drivers of the circadian system, which starts in the brain and regulates physiological rhythms throughout the body’s tissues and organs, affecting hormone levels and the sleep-wake cycle. Light intensity is the amount of light measured over a certain area.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
